Next-generation OLED technologies that will enable brighter and more efficient displays
OLED displays have been gaining popularity rapidly, and are already the dominant smartphone display technology. OLEDs are also the display technology of choice in the smartwatch market, making inroads into the TV, monitor, laptop and tablet markets. The future of the OLED industry looks bright.
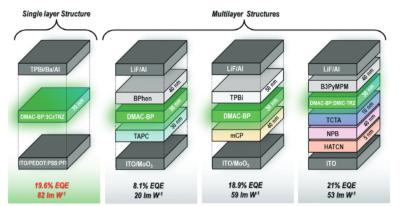
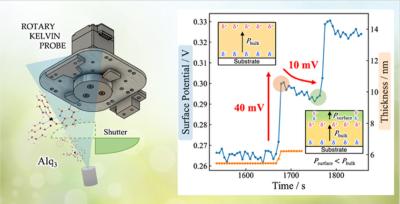
In recent years, the focus of the industry, beyond increasing capacity and reducing production costs, has been improving the performance of OLEDs in the areas of display brightness, efficiency, and lifetime. Brightness is required in many applications - from TVs (for HDR and to view in ambient lighting) through smartphones (outdoor viewing) to automotive, and efficiency is a plus in any scenario (but mostly in mobile displays). Display lifetime is already good enough for many applications, but in some cases (like automotive, and IT displays) it is critical. These three properties usually go together - if you can make more efficient OLED displays, you can drive them at a lower current to achieve the same brightness, and so lifetime increases, or you can achieve higher brightness, etc.





 Now there's a new report in Korea that claims that UDC's blue PHOLED project is facing technical challenges, and UDC is still not able to achieve a long-lasting blue emitter at the right color point. It will be interesting to know whether UDC addresses this issue in its next investor conference call (May 2nd).
Now there's a new report in Korea that claims that UDC's blue PHOLED project is facing technical challenges, and UDC is still not able to achieve a long-lasting blue emitter at the right color point. It will be interesting to know whether UDC addresses this issue in its next investor conference call (May 2nd).