OLED Lifetime: introduction and market status
OLED displays use organic materials that emit light when electricity is applied. OLEDs enable emissive, bright, thin, flexible and efficient displays. OLEDs are set to replace LCDs in all display applications - from small displays to large TV sets.
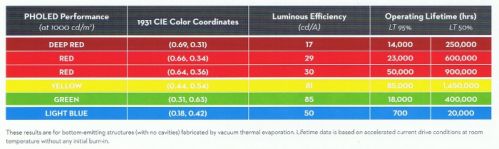
UDC OLED material performance, 2012
One of the main problems of OLED displays is the limited lifetime of the OLED materials. In past years we have seen great advances in this area, and today OLED materials are quite long lasting - with material lifetime reaching million hours or more.
Blue OLED lifetime
A blue OLED emitter is the most unstable emitter, and blue OLEDs (required to create a full-color display) suffer from short lifetimes. This is especially true for the efficient phosphorescent blue emitter - and today there's still no commercial efficient blue emitter.
The OLED industry is seeking several routes to develop an efficient blue. PHOLED pioneer Universal Display is developing a blue PHOLED, but has yet to find a commercial-ready material. Other promising route is TADF emitter technology.
LG to launch screensaver ads on OLED TVs, do owners need to worry about lifetime and burn-in?
LG Electronics is going to add screensaver ads to its TVs, including its high-end OLED TV range. It seemed the company has already started testing this new feature, which shows full-screen ads, and the company will offer a way to turn the ads off, as it markets the new ad system a "feature".
LG Ad Solutions company announced the new "Native Screensaver Ads" feature, that "capitalizes on idle screen time, turning what may be perceived as a period of downtime into a valuable engagement opportunity".
Lordin reports on a highly efficient and stable ultra-pure blue phosphorescent OLED emitter
Researchers from LORDIN, in collaboratioon with researchers from Korea's Dankook University, Gachon University and Hongik University, have reported on a highly efficient and stable ultra-pure blue phosphorescent OLED emitter, based on Lordin's Tetradentate Pt(II) material Complex with a vibration suppression effect.
The researchers say that the new emitter offers a lifetime of 451 hours (LT50 at 1,000 cd/m2), and an EQE of 25.1%. The emission spectrum is extremely narrow - full width at half a maximum of 22 nm. The researchers further developed a tandem OLED device based on this new emitter, which achieves an EQE of 50.3% and a lifetime of 589 hours (LT 70).
Researchers improve the lifetime of OLED devices 4X by adopting a deuterated host material
Researchers from Tsinghua University in Shenzhen, China, have managed to dramatically increase the stability of OLED devices by the adoption of deuterated host material.
The researchers, led by Prof. Man-Chung Tang, have designed and synthesized deuterated anthracene-based hydrocarbon PNA as the new host material. The researchers have observed that the faraday loss decreases with the increase of the deuteration degree.
LG Display to soon commercialize a tandem architecture blue phosphorescence OLED display
A report from Korea says that LG Display has successfully developed an OLED panel that is based on a blue phosphorescence emitter. The blue PHOLED, provided by Universal Display, offers 100% IQE, up from 25% used by current fluorescence emitters. This will result in around 20-30% power saving for the display itself (depending on the images shown).
UDC has been developing blue emitters for many years, and recently the company said that the development will take a few more months and won't be ready in 2024. The main challenge is increasing the lifetime of the materials. However LG Display has adopted a tandem design to enable a commercially ready display, perhaps even sooner than UDC planned.
Next-generation OLED technologies that will enable brighter and more efficient displays
OLED displays have been gaining popularity rapidly, and are already the dominant smartphone display technology. OLEDs are also the display technology of choice in the smartwatch market, making inroads into the TV, monitor, laptop and tablet markets. The future of the OLED industry looks bright.
In recent years, the focus of the industry, beyond increasing capacity and reducing production costs, has been improving the performance of OLEDs in the areas of display brightness, efficiency, and lifetime. Brightness is required in many applications - from TVs (for HDR and to view in ambient lighting) through smartphones (outdoor viewing) to automotive, and efficiency is a plus in any scenario (but mostly in mobile displays). Display lifetime is already good enough for many applications, but in some cases (like automotive, and IT displays) it is critical. These three properties usually go together - if you can make more efficient OLED displays, you can drive them at a lower current to achieve the same brightness, and so lifetime increases, or you can achieve higher brightness, etc.
ETNews: Samsung Display to supply its latest M14 AMOLED panels to Apple and Google
ETNews reports that Samsung Display has developed a new OLED stack, the M14 stack, that it will sell to both Apple and Google to be used in their latest smartphones. The new stack improve the efficiency, lifetime and brightness of the display compared to SDC's previous generation stack.
According to ETNews, the new M14 stack will be used int he upcoming iPhone 16 Pro and Pro Max. Apple's regular iPhone 16 models will use the previous AMOLED stack, Samsung's M12. Google will also adopt the M14 stack in its Pixel 9 (all 3 model types) and the upcoming Pixel Fold 2.
LG Display starts mass producing 13-inch tandem laptop OLED panels
LG Display says that it has started to mass produce tandem OLED laptop panels, the first company to do so. LGD says its tandem architecture double the lifetime of its OLEDs, reduce power consumption by up to 40%, and enable up to three times the brightness.
LGD has been producing tandem OLED displays since 2019, mainly for the automotive industry. This expertise has enabled it to be Apple's main tandem OLED display suppler for its 2024 iPad Pro devices, and now to be the first one to produce tandem laptop panels.
Researchers develop the longest lasting deep-blue CMA TADF OLED emitters
Researchers from the University of Manchester, University of Cambridge and University of Eastern Finland, led by Dr. Alexander Romanov have developed a new deep-blue Carbene-Metal-Amide (CMA) OLED emitter material with promising operating lifetime.
The emitter is based on a a new CMA complex with a rigid amide donor, benzoguanidine. The researcher say that the new design unlocks bright charge-transfer deep-blue emission with 100% photoluminescence quantum yields. The excited state lifetimes of the new CMA complexes are among the lowest reported to date among all TADF emitters
(down to 213 ns), resulting in remarkably fast radiative rates of up to 4.7 × 10 6 s−1 .
The Elec: UDC's blue PHOLED material is still unstable, may delay market introduction
Universal Display Corporation has announced several times that it is progressing with its blue PHOLED material development, and it is on track to release the first commercial material by the end of 2024. In November 2023 we reported that UBI estimates that Samsung has delayed the adoption of a blue PHOLED to the second half of 2025.
 Now there's a new report in Korea that claims that UDC's blue PHOLED project is facing technical challenges, and UDC is still not able to achieve a long-lasting blue emitter at the right color point. It will be interesting to know whether UDC addresses this issue in its next investor conference call (May 2nd).
Now there's a new report in Korea that claims that UDC's blue PHOLED project is facing technical challenges, and UDC is still not able to achieve a long-lasting blue emitter at the right color point. It will be interesting to know whether UDC addresses this issue in its next investor conference call (May 2nd).
BOE commercializes tandem smartphone AMOLED displays to improve lifetime and efficiency
According to reports, BOE has commercialized a new tandem OLED architecture, that enabled an improvement of 40% in power consumption and a 600% increase in display lifetime.
As you can see from the teaser poster above, Chinese smartphone maker Honor will release the first phone to adopt the new panel, the Honor Magic 6 Ultimate, next week on March 18th.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page










