Researchers at the University of St Andrews and the University of Cologne developed a polariton-based OLED device that offers angle-independent narrowband emission.
Polariton-Exciton quasiparticles are created when an OLED material is inserted into a high-quality microcavity. The researchers explain that by sandwiching the OLED device between two "mirrors", strong coupling and hybridization of light and matter can occur. This leads to the creation of the polariton particles.
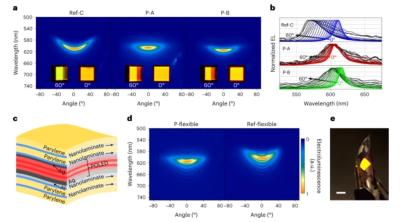
Polariton particles show the high interaction strength of excitons and are readily observable as emitted photons. Thus, polaritons offer a highly attractive platform for various applications. This is the first time that an efficient polariton-emitting OLED device was created, by adding a separate thin film of strongly light-absorbing molecules.
The researchers created red- and green-emitting, narrowband (full-width at half-maximum of less than 20 nm) and spectrally tunable polaritonic OLED devices with up to 10% EQE and high luminance of over 20,000 cd m−2 at 5 V. By optimizing cavity detuning and coupling strength, the researchers achieved emission with ultralow dispersion (<10 nm spectral shift at 60° tilt).