In 2022, Japan Display (JDI) announced that it has developed a "historic breakthrough in display technology" - a new OLED deposition process which they refer to as eLEAP, that is said to be cost effective and can be used to create freeform OLEDs that are brighter, more efficient, and longer lasting compared to OLEDs produced using mask evaporation (FMM).
Japan Display announced an agreement with China-based LCD maker HKC Corp to mass produce panels by 2025 in China, based on JDI's technology, but the plan was later cancelled, and JDI said it will establish its own factory in China. This project saw delays and was scaled-down in December 2023, and yesterday JDI announces that it again delays the project - now hoping to sign the agreement with the Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone by October 2024.
JDI is reportedly aiming to build a single 8.7-Gen (30,000 monthly substrates) production line in Wuhu (originally it planed to establish an additional 6-Gen line). In 2023 the company says it hopes the 8.7-Gen line will start mass production in December 2026, but with the new delays, it will likely only enter full production in 2027.
We do not know the cause of the latest delay. It could be that the Anhui government hasn't yet decided on this project's viability, and it could be that JDI is struggling to fully develop the eLEAP technology and get it ready for commercialization.
JDI has started be developing eLEAP displays for wearables (as this is its current main AMOLED panel type, which it is supplying to Apple's Watch devices), and has later moved to develop eLEAP for use in laptop displays (14-inch displays). The company is now producing eLEAP samples in its Japan fab, and it says that the performance exceeds customer expectations.
The new fab in China will increase its production volume dramatically, of course. If JDI looks to build a 8.7-Gen line only, it may be that it no longer aims to produce wearable eLEAP displays. We assumed this was due to Apple's move to adopt microLED displays in its highest-end smartwatch displays in 2026. Apple since cancelled its plans to produce a microLED wearable display.
Japan Display was established in 2011 by the merger of Sony's, Toshiba's and Hitachi's display businesses and funded by Japan's government fund Innovation Network Corporation (INCJ). The company was late to realize the importance of OLED production and has struggled financially for many years. It announced a strategic focus on OLED displays in 2017, but never managed to gain major mass production capabilities. The company started to produce OLED displays in 2019, but with low volume. It managed to gain Apple as a customer for Watch wearable displays. This new partnership with HKC could be great news for the company, finally gaining access to the vast amounts of money required to mass produce AMOLEDs.
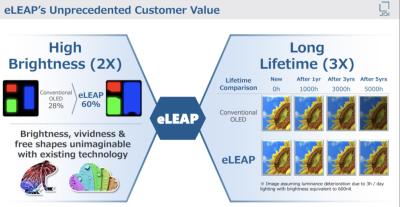
eLEAP is based on a lithographic method, and does not require any masks. The main advantage seems to be that OLED displays produced by eLEAP technology can achieve an aperture ratio of 60%, compared with FMM OLEDs which achieve a ratio of about 28%. This means that the OLED displays can be driven at lower currents - which extends the lifetime, improves the efficiency and also enables higher-peak brightness when needed.
JDI claims that eLEAP displays offer a boost of 2X in emission efficiency and peak brightness - while lifetime is extended by of 3X (which also reduces burn-in problems). These numbers, if accurate, are highly impressive. JDI is using a 300PPI display for these calculations.
eLEAP stands for environment positive, Lithography with maskless deposition, Extreme long life, low power, and high luminance, and Any shape Patterning. JDI says that eLEAP can be combined with the company's HMO (High Mobility Oxide) backplane technology to dramatically improve OLED display performance. eLEAP production technology can be scaled up to 8-Gen (2200x2500 mm) substrates - or even larger, and is suitable for OLED display production from wearable-size displays to TV sizes.

Finally, JDI says that eLEAP reduces operating costs, reduces material waste and does not require cleaning fluids for the masks - which means that eLEAP significantly reduces material usage, waste and CO2 emissions.
In 2022 it was reported that Samsung Display is interested in JDI's eLeap technology, but this wasn't confirmed since then, and later reports suggest at SDC is interested in an exclusive license, which JDI does not wish to provide.
Maskless OLED production technology could provide a dramatic increase in performance in addition to cost reductions - and is an important trend to watch in the industry. The OLED Toolbox (updated yesterday) provides more details and thoughts on maskless OLED production and is a must tool for OLED professionals aiming to stay updated and understand where the OLED industry is heading.