TADF OLED emitters, or Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence, is a relatively new class of OLED emitter materials that promise efficient and long-lifetime performance without any heavy metals. TADF research started in earnest in 2012, and the first TADF emitters reached commercial status at the end of 2019.
There are currently three main challenges with OLED emitters that TADF aims to solve - an efficient and long-lasting blue color emitter, low cost alternatives current red and green emitters and the development of soluble OLEDs that can be deposited using low cost ink-jet printing or other "wet" methods.
TADF is being developed by several companies. Japan-based Kyulux was established to commercialize Prof. Adachi's HyperFluoresence technology, which combines two emitter systems, TADF and Fluorescence. Germany-based Cynora is focusing on a blue TADF emitter. Both companies are working hard to achieve commercial-ready materials. While a blue TADF (or HyperFluoresence) emitter is not here yet, in late 2019 Kyulux and Wisechip brought to market the first OLED with a yellow HF emitter.
Idemitsu Kosan also considers TADF as one of the key OLED technologies and intends to focus on TADF in the future. In late 2019 Idemitsu together with Toray announced the world's most efficient red OLED emitter - based on Idemitsu's TADF/HF material. UDC has been recently awarded a patent on TADF materials, although the company says that TADF is not in its focus.
The EU launched two TADF related collaborative research projects to focus on TADF emitters, Project HyperOLED and the 2015 project Phebe.
The latest TADF news:
Kyulux says it is on track to commercialize green Hyperfluorescence materials in 2023, red and blue in 2024
Kyulux gave a very upbeat presentation at SID Displayweek, during which it updated on its latest material specification and its commercialization plans.
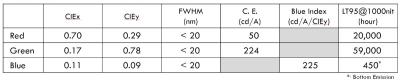
Kyulux managed to increase the lifetime of its Hyperfluorescence emitter systems (which features an IQE of 100% and a narrow emission spectrum) quite dramatically in the past year its green material now offers a lifetime of 59,000 hours (LT95@1000 nits, top emission), while the red material is at 20,000 hours. The blue material has also increase from280 hours to 450 hours in the past year.
SolOLED secures $250,000 to develop novel TADF emitters
UK-based SolOLED secured 200,000 GBP (almost $250,000 USD) in new funding from Scottish Enterprise to commercialize its novel OLED TADF emitter materials. SolOLED is launching a collaborative research project with CENSIS to commercialize the materials.
SolOLED was established in 2021 in the UK, to develop a family of novel solution-based TADF OLED emitter, based on technology that originated from the University of St. Andrews.
TADF developer Noctiluca IPOs at the Poland NewConnect stock exchange
Poland-based TADF developer Noctiluca went public at the Polish NewConnect stock exchange last week. The company now trades under the NCL ticker.
Noctiluca did not raise any funds in this IPO, as it has no need for more funds at this stage, but this move will enable some stock holders to realize their funds and other to join as stakeholders in the company.
OLED innovation in Poland - 2022 status and future plans
Poland is aiming to become a major innovation and high-tech hub, and the country is already enjoying a growing industry, focusing on IT, bio-technology, robotics and nanotechnology.
Poland has a strong material science and development expertise, and in recent years we have been seeing OLED and display-related ventures out of Poland. It seems Poland is poised to become an interesting location to watch for future innovation in the OLED industry.
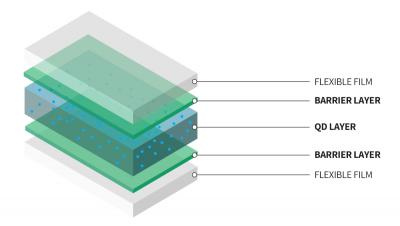
Ergis Group noDiffusion OLED encapsulation film
One such company is the Poland-based Ergis Group, a leader in plastic processing active in markets such as food packaging, industrial, automotive, medical and more. In 2020, Ergis launched its first product for the optoelectronic applications (such as the display market and photovoltaics) - the Ergis noDiffusion films for flexible OLED panels (both displays and lighting) and OPVs. Ergis is using a unique ALD-based technology that enables it to offer high performance films on low cost PET films.
How machine learning and AI help find next-generation OLED materials
In recent years, we have seen accelerated OLED materials development, aided by software tools based on machine learning and Artificial Intelligence. This is an excellent development which contributes to the continued improvement in OLED efficiency, brightness and lifetime.
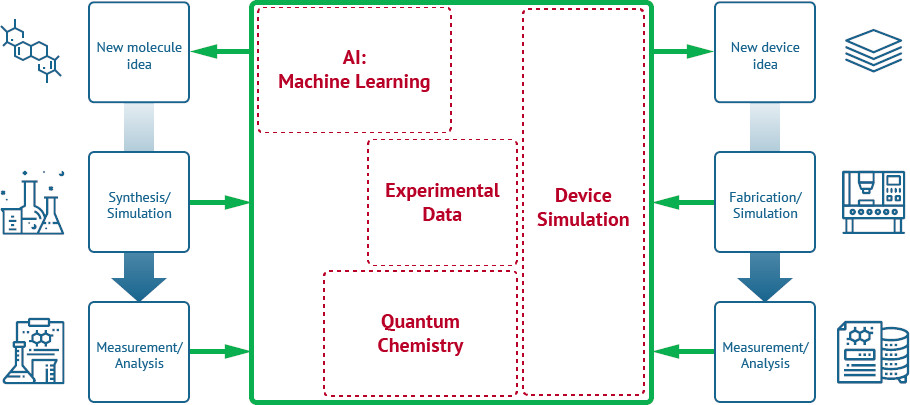
Kyulux's Kyumatic AI material discover system
The promise of these new technologies is the ability to screen millions of possible molecules and systems quickly and efficiently. Materials scientists can then take the most promising candidates and perform real synthesis and experiments to confirm the operation in actual OLED devices.
Interview with Dr. Michael Doran, CEO & Founder at Notion Systems
Notion Systems is a leading supplier of industrial ink jet printing systems. The n.jet inkjet platform from Notion Systems is used to produce printed circuit boards, OLED & QLED displays, sensors and high-quality 3D parts.

We present the following interview with the Company's CEO and founder, Dr. Michael Doran.
Q: Hello Michael. Can you detail notion systems' offering for the OLED industry? We understand you offer R&D and production systems, for both RBG printing and TFE printing.
Notion Systems offers a system platform called n.jet display series that prints functional layers at various steps of display production and for a range of display technologies. These include rigid, flexible, OLED, QLED and micro displays. The platform meets the most stringent requirements for process environment and process stability.
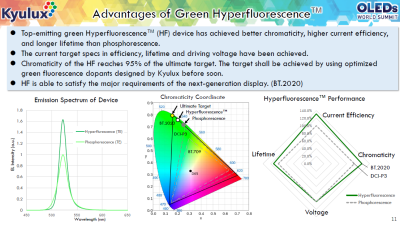
Kyulux: our green Hyperfluoresence emitter is getting close to commercialization
Hyperfluoresence emitter system developer Kyulux announced that its green material is getting close to commercialization. The company is now working closely with OLED makers, preparing for early adoption.
Kyulux says that its green emitter has not only met the required performance of OLED panel makers, in terms of efficiency, lifetime and driving voltage - but has actually surpassed the performance of green phosphorescent emitters in top emission devices. The green HF device achieves higher current efficiency, longer lifetime and offers a narrow emission spectrum and can thus enable better chromaticity.
Kyulux reveals its latest TADF material performance
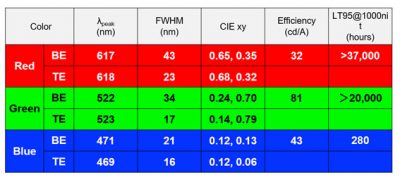
During SID Display Week 2021, Kyulux detailed its latest TADF material performance. The red and green materials are "close to commercialization", and the company reports "excellent progress" with its blue emitter.
Using simulations, Kyulux shows how its Hyperfluorescence system is more efficient than a comparable phosphorescence emitter. While both emitters feature pretty much the same EQE, the narrow spectrum of the HF system which results in higher light intensity and can enable more efficient displays - by around 10%, according to Kyulux.
Kyulux raises $34 million in its latest funding round, receives basic HF TADF patent from Kyushu University
TADF materials developer Kyulux announced that it has finalized its Series-B-prime funding round, raising $34.3 million USD from several VCs and companies. Kyulux will be able to now accelerate its product development and drive for adoption of its materials in smartphone OLED displays.

Kyulux also announced plans to establish a mass production system for its materials, in cooperation with chemical companies.
Densely-packaged dimer-enhanced MR-TADF emitters demonstrate high efficiency with a narrow emission spectrum
Researchers from Soochow University, in collaboration with a wide team of scientists from China and Japan (including Prof. Adachi from Kyushu University) developed a TADF emitter material compound that features high efficiency and a narrow color spectrum.
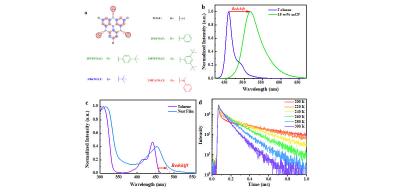
Up until now, most TADF emitters featured a wide spectrum, which limits the adoption of TADF materials in displays as they cannot enable a wide color spectrum. To overcome this problem companies employ a structure in which the TADF emitter is combined with a narrow-spectrum fluorescence emitter (so-called Hyperfluorescence).
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
- Next page